Powering Perspectives: Exploring Electrical Imagery in Everyday Life
Powering Perspectives: Exploring Electrical Imagery in Everyday Life
Hello Friends,
Discover the intricate workings and multifunctional capabilities of the Energy P543 relay in safeguarding electrical power systems. Explore its key functions, applications, and role in ensuring system reliability.
Introduction to Energy P543 Relay
The Energy P543 relay is a microprocessor-based protection relay that offers advanced protection, control, and monitoring capabilities for electrical networks. It is widely used in medium and high-voltage power systems, including substations, industrial plants, and distribution networks, to safeguard equipment and personnel from electrical faults and disturbances.
Working Principles
The Energy P543 relay operates based on the principle of measuring electrical parameters such as voltage, current, frequency, and power factor to detect abnormal conditions in the system. It continuously monitors these parameters and compares them against predefined threshold values to identify potential faults or disturbances.
Key Functions
- Overcurrent Protection: One of the primary functions of the Energy P543 relay is to provide overcurrent protection, which involves detecting excessive current flow in the system due to short circuits, overloads, or ground faults. When the current exceeds a preset threshold, the relay initiates a trip signal to isolate the faulty section of the network by opening the associated circuit breaker.
- Voltage Protection: The Energy P543 relay also offers voltage protection capabilities to safeguard equipment from voltage fluctuations, overvoltages, and undervoltages. It monitors the voltage levels within the system and triggers protective actions if the voltage exceeds or falls below acceptable limits, thereby preventing damage to sensitive equipment.
- Frequency Protection: In addition to current and voltage protection, the Energy P543 relay provides frequency protection to ensure system stability and reliability. It monitors the frequency of the electrical supply and initiates corrective measures if deviations from the nominal frequency occur, such as underfrequency or overfrequency conditions.
- Distance Protection: The Energy P543 relay offers distance protection features to detect and locate faults in transmission lines based on impedance measurements. By analyzing the impedance characteristics of the line, the relay can accurately determine the distance to the fault and coordinate with neighboring relays to isolate the faulted section of the line.
- Control and Monitoring: Apart from protection functions, the Energy P543 relay also provides control and monitoring capabilities, allowing operators to remotely supervise and manage the electrical system. It offers real-time data visualization, event logging, and communication interfaces for seamless integration into supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems.
- The Energy P543 relay finds applications in various sectors of the electrical industry, including:
- Power generation plants
- Transmission and distribution substations
- Industrial facilities
- Renewable energy systems
- Railways and transportation networks
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Energy P543 relay is a versatile and reliable protection device that plays a critical role in ensuring the safety, stability, and efficiency of electrical power systems. With its advanced features, including overcurrent, voltage, frequency, and distance protection, the relay offers comprehensive protection against electrical faults and disturbances, minimizing downtime and enhancing system reliability. As technology continues to evolve, the Energy P543 relay remains at the forefront of electrical protection, providing innovative solutions to meet the evolving needs of the power industry.
Explore the essential workings and multifunctional capabilities of the Energy PT32 relay in safeguarding electrical power systems. Discover its key functions, including overcurrent and voltage protection, fault detection, and communication interfaces, ensuring system reliability and integrity.
The Energy PT32 relay is a vital component in electrical power systems, serving as a protective device to ensure the safe and reliable operation of electrical networks. Designed with advanced technology and multiple functions, the PT32 relay plays a crucial role in detecting and mitigating various fault conditions and abnormalities within the system. Let's explore the working principles and key functions of the Energy PT32 relay in more detail.
Working Principles
The Energy PT32 relay operates based on the principle of monitoring electrical parameters such as voltage, current, frequency, and power factor to identify abnormal conditions within the system. Using sophisticated algorithms and signal processing techniques, the relay continuously analyzes these parameters to detect potential faults or disturbances.
Key Functions
- Overcurrent Protection: One of the primary functions of the Energy PT32 relay is to provide overcurrent protection. It monitors the current flowing through electrical circuits and activates protective measures when the current exceeds predefined threshold values. This helps prevent damage to equipment and minimizes the risk of electrical fires caused by excessive currents.
- Voltage Protection: The PT32 relay offers voltage protection capabilities to safeguard equipment from voltage variations, overvoltages, and undervoltages. By monitoring voltage levels within the system, the relay can initiate corrective actions to maintain voltage stability and protect sensitive equipment from damage.
- Frequency Protection: In addition to current and voltage protection, the Energy PT32 relay provides frequency protection features. It monitors the frequency of the electrical supply and triggers protective measures in the event of deviations from the nominal frequency. This helps maintain system stability and reliability, particularly in grid-connected applications.
- Fault Detection: The PT32 relay is equipped with fault detection algorithms to identify various types of faults, including short circuits, overloads, and earth faults. By accurately detecting and locating faults within the system, the relay can initiate rapid isolation and restoration procedures to minimize downtime and maintain system integrity.
- Communication and Monitoring: The Energy PT32 relay is equipped with communication interfaces, allowing it to communicate with other devices and systems within the network. This enables remote monitoring and control, facilitating real-time data visualization, event logging, and diagnostic analysis for enhanced system management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Energy PT32 relay is a versatile and indispensable component in electrical power systems, providing essential protection and control functions to ensure the safe and reliable operation of electrical networks. With its advanced technology and multifunctional capabilities, the PT32 relay plays a crucial role in safeguarding equipment, minimizing downtime, and maintaining system integrity in diverse applications across the power industry.
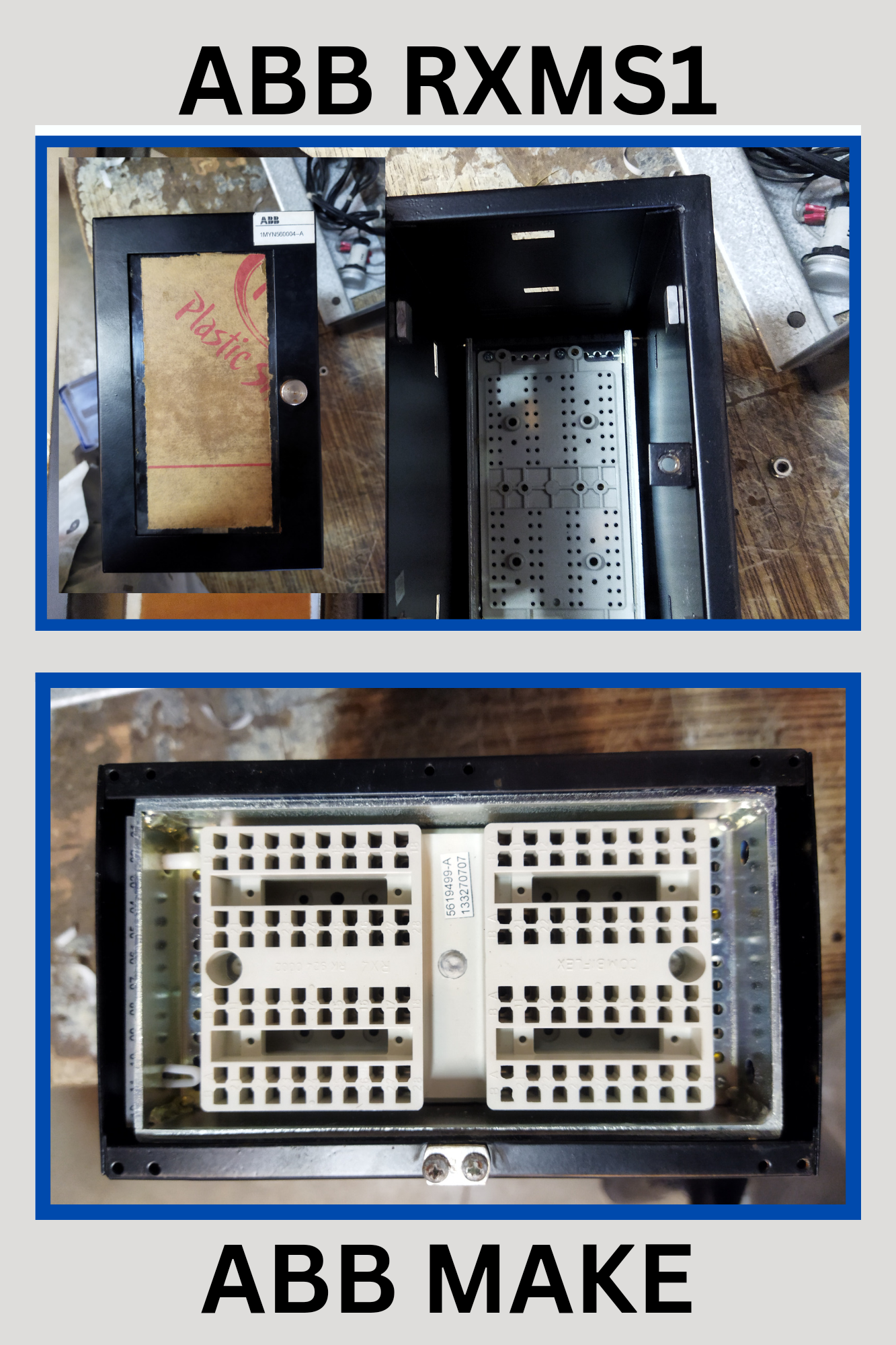
The ABB RXMS1 relay is a versatile and advanced protection device used in electrical power systems to ensure the safe and reliable operation of electrical networks. Designed with cutting-edge technology and comprehensive functionality, the RXMS1 relay offers a wide range of protection features to detect and mitigate various fault conditions and abnormalities within the system. Let's delve into the working principles and key functions of the ABB RXMS1 relay.
Working Principles
The ABB RXMS1 relay operates based on the principle of continuous monitoring and analysis of electrical parameters such as voltage, current, frequency, and phase angle. Using advanced algorithms and signal processing techniques, the relay evaluates these parameters in real-time to detect abnormal conditions indicative of potential faults or disturbances in the system.
Key Functions
- Overcurrent Protection: One of the primary functions of the ABB RXMS1 relay is to provide overcurrent protection. It continuously monitors the current flowing through electrical circuits and activates protective measures when the current exceeds preset threshold values. This helps prevent equipment damage and minimizes the risk of electrical hazards caused by excessive currents.
- Voltage Protection: The RXMS1 relay offers voltage protection capabilities to safeguard equipment from voltage variations, overvoltages, and undervoltages. By monitoring voltage levels within the system, the relay can initiate corrective actions to maintain voltage stability and protect sensitive equipment from damage.
- Frequency Protection: In addition to current and voltage protection, the ABB RXMS1 relay provides frequency protection features. It monitors the frequency of the electrical supply and triggers protective measures in the event of deviations from the nominal frequency. This helps maintain system stability and reliability, particularly in grid-connected applications.
- Fault Detection: The RXMS1 relay is equipped with advanced fault detection algorithms to identify various types of faults, including short circuits, overloads, and earth faults. By accurately detecting and locating faults within the system, the relay can initiate rapid isolation and restoration procedures to minimize downtime and maintain system integrity.
- Communication and Monitoring: The ABB RXMS1 relay features communication interfaces, allowing it to communicate with other devices and systems within the network. This enables remote monitoring and control, facilitating real-time data visualization, event logging, and diagnostic analysis for enhanced system management.
conclusion
The ABB RXMS1 relay is a crucial component in electrical power systems, providing essential protection and control functions to ensure the safe and reliable operation of electrical networks. With its advanced technology and comprehensive functionality, the RXMS1 relay plays a vital role in safeguarding equipment, minimizing downtime, and maintaining system integrity in various applications across the power industry.
- Versatile Compatibility: The EMRT 213 is compatible with a wide range of relay types and models, making it suitable for testing various relay configurations used in power distribution, generation, and transmission systems.
- Multiple Test Functions: This test block offers comprehensive testing capabilities, including functionality tests, timing tests, and performance verification tests for relays under different operating conditions.
- Precise Timing Measurement: The EMRT 213 is equipped with high-precision timing circuits and measurement capabilities, allowing users to accurately assess relay response times, pickup and dropout characteristics, and trip/reset sequences.
- User-Friendly Interface: Featuring intuitive controls and a user-friendly interface, the EMRT 213 simplifies the testing process and enhances operator efficiency. It may include digital displays, push-button controls, and status indicators for easy operation and monitoring.
- Portable Design: The compact and lightweight design of the EMRT 213 makes it portable and suitable for on-site testing and troubleshooting tasks. It may come with carrying handles or mounting options for added convenience.
- Safety Features: To ensure operator safety and equipment protection, the EMRT 213 may incorporate built-in safeguards such as overload protection, short-circuit protection, and insulation monitoring mechanisms.
- Trip Signal Generation: The REL 91263 is responsible for generating trip signals to initiate the opening of circuit breakers in response to abnormal operating conditions, such as overcurrent, short circuits, or system faults. It detects fault conditions and activates the trip mechanism to isolate the faulty section of the electrical network, thereby preventing damage to equipment and ensuring personnel safety.
- Coordination with Protective Devices: The REL 91263 coordinates with other protective devices, such as overcurrent relays, differential relays, and distance relays, to ensure proper sequencing and coordination of protective actions. It communicates with these devices to synchronize trip commands and maintain system stability during fault conditions.
- Supervision and Monitoring: In addition to trip signal generation, the REL 91263 provides supervision and monitoring functions to continuously monitor the status and health of circuit breakers and associated protective devices. It detects abnormalities, such as breaker failure or trip circuit faults, and initiates appropriate alarm signals or corrective actions to address the issue.
- Communication Interfaces: The REL 91263 may feature communication interfaces, such as digital communication protocols (e.g., IEC 61850), Modbus, or Ethernet, to enable remote monitoring and control of relay operations. This allows operators to access real-time status information, perform diagnostics, and configure relay settings from a centralized control center.
- Programmable Logic: Some variants of the REL 91263 may incorporate programmable logic capabilities, allowing users to customize relay functions and logic algorithms based on specific application requirements. This flexibility enables the adaptation of the relay to different system configurations and operational scenarios.
- Trip Signal Generation: The REL VD3X110 is responsible for generating trip signals to initiate the opening of circuit breakers in response to abnormal operating conditions, such as overcurrent, short circuits, or system faults. It detects fault conditions and activates the trip mechanism to isolate the faulty section of the electrical network, preventing damage to equipment and ensuring personnel safety.
- Coordination with Protective Devices: The REL VD3X110 coordinates with other protective devices, such as overcurrent relays, differential relays, and distance relays, to ensure proper sequencing and coordination of protective actions. It communicates with these devices to synchronize trip commands and maintain system stability during fault conditions.
- Supervision and Monitoring: In addition to trip signal generation, the REL VD3X110 provides supervision and monitoring functions to continuously monitor the status and health of circuit breakers and associated protective devices. It detects abnormalities, such as breaker failure or trip circuit faults, and initiates appropriate alarm signals or corrective actions to address the issue.
- Communication Interfaces: The REL VD3X110 may feature communication interfaces, such as digital communication protocols (e.g., IEC 61850), Modbus, or Ethernet, to enable remote monitoring and control of relay operations. This allows operators to access real-time status information, perform diagnostics, and configure relay settings from a centralized control center.
- Programmable Logic: Some variants of the REL VD3X110 may incorporate programmable logic capabilities, allowing users to customize relay functions and logic algorithms based on specific application requirements. This flexibility enables the adaptation of the relay to different system configurations and operational scenarios.
- Temperature Sensor: The thermostat is equipped with a temperature sensor, usually a bimetallic strip, thermistor, or electronic sensor, that detects changes in temperature.
- Setpoint Control: Users can set a desired temperature, known as the setpoint, using the thermostat's control interface. The thermostat continuously compares the current temperature to the setpoint and activates heating or cooling systems as needed to maintain the desired temperature.
- Switching Mechanism: When the temperature deviates from the setpoint, the thermostat triggers a switching mechanism to turn the heating or cooling system on or off. This may involve activating a relay, contactor, or electronic switch to control the flow of electricity to the HVAC equipment.
- Display: Many modern thermostats feature a digital display that shows the current temperature, setpoint, and other relevant information. Some thermostats also offer advanced features such as programmable schedules, energy usage tracking, and Wi-Fi connectivity for remote monitoring and control.
- Mode Selection: Thermostats may offer different operating modes, such as heating, cooling, fan-only, or automatic mode. Users can select the appropriate mode based on their heating and cooling needs.
- User Interface: The thermostat's user interface allows users to adjust settings, set schedules, and access additional features. This may include buttons, knobs, touchscreens, or smartphone apps for wireless control.
- Heating Element: Space heaters utilize different types of heating elements to generate heat, including ceramic heating elements, quartz tubes, metal coils, or oil-filled radiators. When electricity is supplied to the heating element, it generates heat, which is then distributed into the surrounding space.
- Housing: The housing of a space heater is typically made of metal or durable plastic and is designed to enclose the heating element safely. It often includes grilles or vents to allow airflow and prevent the unit from overheating.
- Controls: Most space heaters feature controls that allow users to adjust the temperature, fan speed, and other settings. These controls may include knobs, buttons, or digital displays for precise temperature adjustments.
- Safety Features: To prevent accidents and ensure safe operation, space heaters are equipped with various safety features, such as tip-over protection, overheat protection, and automatic shut-off mechanisms. Tip-over protection automatically turns off the heater if it is knocked over, while overheat protection shuts off the unit if it reaches an unsafe temperature.
- Fan: Some space heaters are equipped with built-in fans to help distribute heat more evenly throughout the room. These fan-forced heaters blow air over the heating element, accelerating the warming process and improving heat distribution.
- Portability: One of the main advantages of space heaters is their portability. They are typically lightweight and compact, making them easy to move from one room to another as needed. Some models also feature integrated handles or wheels for added convenience.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern space heaters often incorporate energy-saving features, such as programmable timers, adjustable thermostats, and eco modes, to help reduce energy consumption and lower heating costs.
- Button: The main component of an emergency push button is the large, prominently placed button that operators can push to initiate an emergency stop. The button is typically colored bright red for easy visibility and is often marked with the universal symbol for an emergency stop (a white triangle inside a red circle).
- Enclosure: The push button is housed within a sturdy and durable enclosure, usually made of metal or plastic, to protect it from damage and ensure reliable operation in harsh environments. The enclosure is designed to be resistant to water, dust, and other contaminants.
- Normally Closed Contacts: Inside the enclosure, the emergency push button is connected to a set of electrical contacts that are normally closed. When the button is pressed, these contacts open, interrupting the flow of electricity to the machinery or equipment, and triggering the emergency stop.
- Reset Mechanism: After the emergency stop has been activated, the emergency push button typically features a reset mechanism that must be manually operated to reset the contacts and restore power to the machinery or equipment. This prevents accidental restarts and ensures that the equipment is only restarted intentionally by authorized personnel.
- Lockout/Tagout Capability: Some emergency push buttons are equipped with a lockout/tagout mechanism that allows them to be locked in the deactivated position to prevent unauthorized access or tampering. This helps to ensure that the equipment remains safely shut down during maintenance or repair procedures.
- Construction: The LT bar is usually made of high-quality copper or aluminum material, chosen for its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. Copper is the preferred material due to its superior conductivity, but aluminum is also used in some applications where cost considerations are important.
- Mounting: The LT bar is mounted securely within the electrical enclosure or panel using fasteners such as screws, bolts, or clips. It is positioned in a central location to facilitate easy access and connection to grounding conductors.
- Connection Points: The LT bar features multiple connection points, typically in the form of threaded holes or terminal lugs, where grounding conductors, cables, or wires can be securely attached using bolts or screws. These connection points allow for the termination of grounding conductors from various electrical circuits and equipment.
- Grounding Conductors: Grounding conductors, usually made of copper or aluminum, are connected to the LT bar and extend to ground rods, grounding electrodes, or other grounding systems installed in the earth. These conductors provide a low impedance path for fault currents to flow safely into the ground, preventing electric shocks, equipment damage, and fire hazards.
- Labels and Markings: The LT bar may be labeled or marked with relevant information, such as its rated current capacity, material composition, manufacturer's name, and electrical specifications, to ensure proper installation and compliance with safety standards.
- Compliance: Earthing LT Bars must comply with relevant electrical codes, standards, and regulations, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards, and local building codes, to ensure safety and reliability in electrical installations.
- Display Panels: The annunciator typically consists of one or more display panels equipped with indicator lights, LEDs (Light-Emitting Diodes), or alphanumeric displays. These panels are used to convey information about the status of monitored parameters or equipment, such as process variables, alarms, faults, or warnings.
- Alarm Inputs: The annunciator is connected to various sensors, switches, or monitoring devices throughout the facility, which detect abnormal conditions or events. These inputs trigger the activation of the corresponding indicator lights or alarms on the annunciator panel when predefined thresholds or conditions are met.
- Alarm Logic: The annunciator features built-in logic or programming that determines how alarms are prioritized, acknowledged, and displayed. It may incorporate features such as alarm prioritization, alarm grouping, latching, and acknowledgment to ensure that operators can quickly identify and respond to critical alarms.
- Audible Alarms: In addition to visual indicators, the Alan make annunciator may also include built-in audible alarms or sounders to provide supplementary alerts to operators in noisy environments or situations where visual cues may be insufficient.
- Controls and Interfaces: The annunciator may include controls and interfaces for operators to interact with the system, such as alarm acknowledgment buttons, reset switches, test functions, and configuration menus. These controls allow operators to acknowledge alarms, silence audible alerts, or perform diagnostic checks.
- Enclosure: The annunciator is housed within a durable and weather-resistant enclosure, typically made of metal or high-impact plastic, to protect the internal components from environmental factors, dust, moisture, and mechanical damage.
- Mounting Options: The Alan make annunciator may offer various mounting options, such as wall mounting, panel mounting, or rack mounting, to accommodate different installation requirements and space constraints in control rooms or equipment cabinets.












Post a Comment